The following links will provide you with guides (pictures and video) on how to use for OODP, MDP or any other projects basically
(Note: The sample project showcased here is a Gradle Java Project , but most of the instructions are generic and works with any languages with the exception of importing cloned repositories)
Take note that the icons beside each link (e.g , or ) denotes which VCS provider or software is relevant for the guide
Being a Version Control System (VCS) and a VCS provider respectively, they allow us to be able to collaborate on the same codebase simultaneously with support for History (through the Commits system) and conflict resolution
YES! However, this guide is catered to SourceTree but other GUI programs will have their own equivalent features. You just have to hunt for them. Or you can always use console 😏
Scroll all the way down to the bottom of each page and I will add the console command equivalent there if available
These terms refers to various repositories that is registered. origin refers to your own repository where you are currently editing your codebase in. upstream refers to the parent repository for a forked repository. A forked repository is the term used for repositories that have been cloned to your own profile
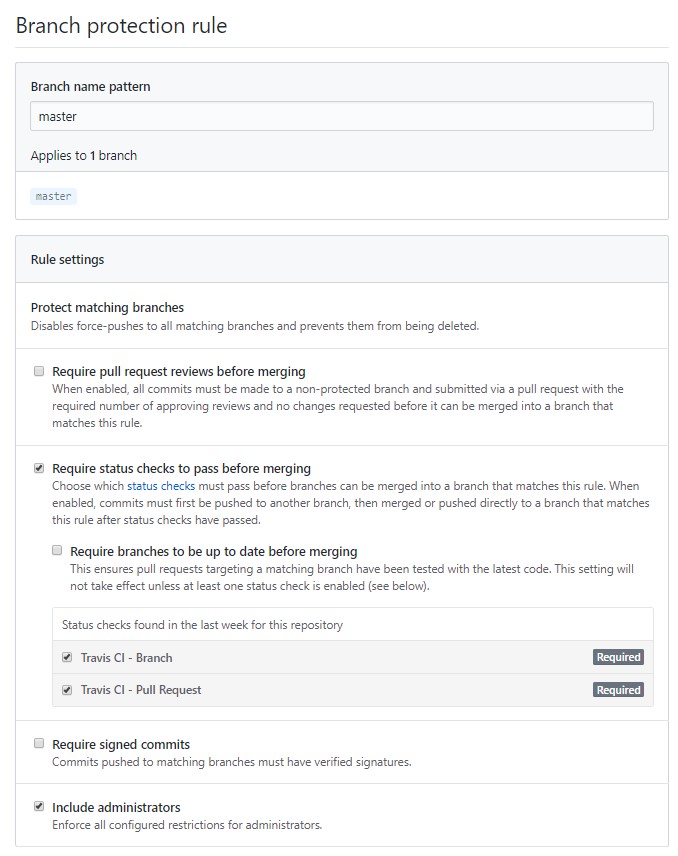
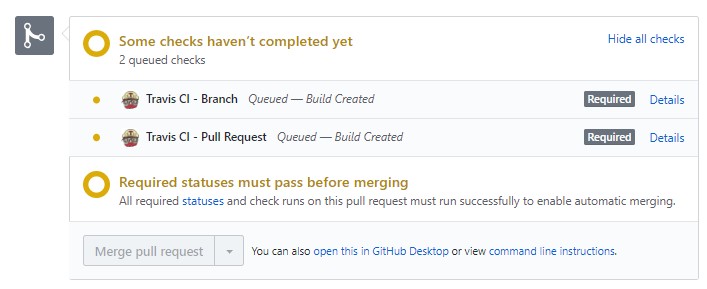
The main reason for working in seperate branches is to allow us to be able to work on the codebase simultaneously without much conflicts (hopefully). It is also done to ensure that the master branch will always be compilable and bad code does not land there. This is why branch protection exists as well to prevent direct pushes


Atlassian's Official "Get Started with SourceTree" Guide
Workflows: BitBucket /GitHub /GitLab
We have an extremely useful tutorial lecture available on YouTube courtesy of MIT
Note: This is only for project members. It will not be relevant to any public viewers. So please ignore if you are not a related Project Member